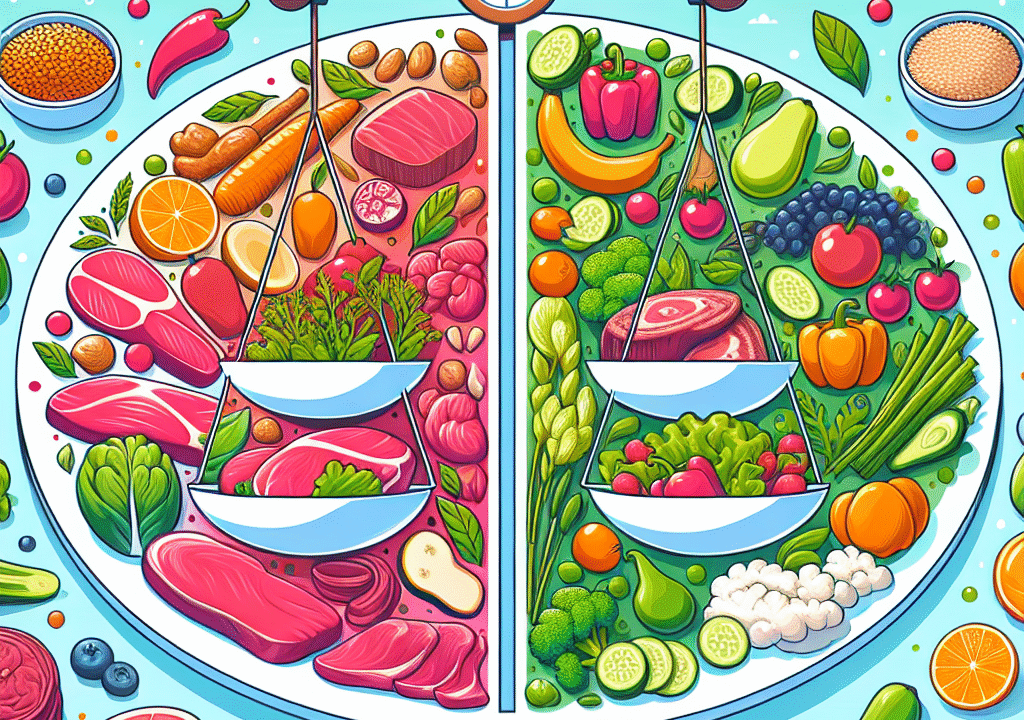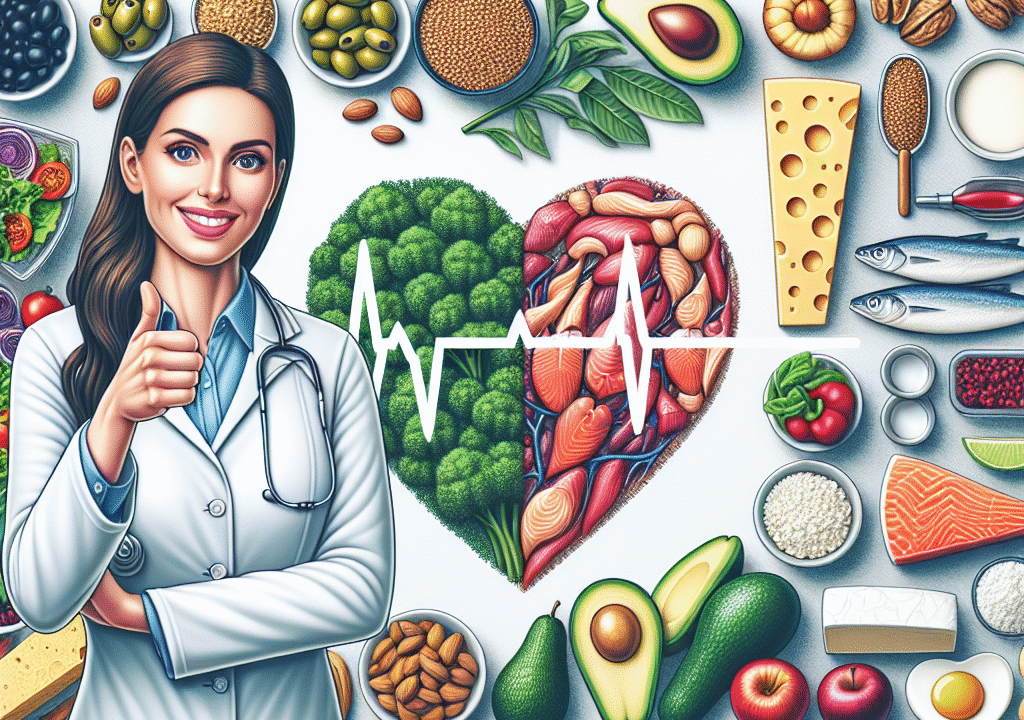Keto 2.0: A Healthier, More Sustainable Way to Go Low-Carb
A Fresh Take on Low-Carb Living
Over the past few years, the classic ketogenic diet has gained massive popularity. Originally designed to manage epilepsy, traditional keto evolved into a widespread weight-loss trend because of its fat-burning benefits. However, it also comes with drawbacks: high levels of saturated animal fats and extreme carbohydrate restriction make it difficult for many to stick with long term.
That’s where Keto 2.0 enters the picture. Also referred to as plant-based keto or clean keto, this modernized version retains the fat-burning advantages of ketosis while incorporating healthier food options, improved flexibility, and a nutrient-dense foundation. According to registered dietitian Maggie Michalczyk, RDN, “Keto 2.0 is a gentler, more inclusive approach that can help people stick to low-carb living without harming their health.”
This article breaks down what Keto 2.0 is, how it differs from the original keto plan, and how to adopt it as a sustainable lifestyle.
What Is Keto 2.0?
At its core, Keto 2.0 is a flexible, plant-focused evolution of the conventional ketogenic diet. It emphasizes:
– Whole, minimally processed foods
– Plant-based proteins and healthy fats
– High-fiber, nutrient-dense ingredients
– Moderate carbohydrate intake from non-starchy vegetables and select fruits
Unlike the traditional keto approach that relies heavily on fatty meats, cheese, and butter, Keto 2.0 prioritizes unsaturated fats from sources such as avocado, chia seeds, olive oil, and nuts. This shift aligns better with modern dietary guidelines and supports heart health.
A 2021 study published in Frontiers in Nutrition found that diets rich in unsaturated fats and low-glycemic, high-fiber foods are linked to lower inflammation and improved metabolic health. This research supports the idea that Keto 2.0 can offer benefits for both well-being and longevity.
Rebalanced Macros for Better Nutrition
Traditional ketogenic diets are composed of approximately:
– 70 to 75 percent fat
– 20 to 25 percent protein
– 5 to 10 percent carbohydrates
Keto 2.0 offers a more balanced approach:
– 50 to 60 percent fat
– 30 to 35 percent protein
– 10 to 15 percent carbohydrates
While the goal remains achieving ketosis—where the body uses fat instead of glucose for energy—Keto 2.0 reaches this state through nutrient-dense, high-fiber foods with heart-healthy fat sources.
Instead of starting your day with bacon and eggs, a typical Keto 2.0 breakfast might include a veggie scramble cooked in olive oil, half an avocado, and a handful of nuts. It’s a healthier, more diverse start that supports long-term success.
Why Keto 2.0 Is Easier to Stick With
One of the biggest challenges of traditional keto is sustainability. Research shows that more than 50 percent of people abandon the keto diet within six months, often due to its strict rules and limited food choices.
Keto 2.0 addresses common barriers:
– Food Monotony → Offers variety with low-carb legumes, berries, and moderate amounts of whole grains like quinoa
– Digestive Issues → Focuses on fiber-rich foods like leafy greens, chia seeds, and cauliflower to support gut health
– Social Restrictions → Provides more dietary flexibility for dining out or travel
– Weight Plateaus → Nutrient-dense foods help reduce inflammation and improve metabolism
Dr. Will Cole, functional medicine expert and author of Ketotarian, explains it best: “Keto doesn’t have to be a meat-fest. Keto 2.0 gives people a path to ketosis that also supports their gut health, hormone balance, and long-term happiness.”
The Best Foods for Keto 2.0
Transitioning to a cleaner version of keto means choosing foods that nourish your body while keeping your carb intake low. Here are top picks for your Keto 2.0 grocery list:
Proteins (Opt for lean or plant-based when possible):
– Fatty fish like salmon and sardines – packed with omega-3s
– Organic poultry such as chicken or turkey breast
– Plant-based proteins including tofu, tempeh, and small portions of legumes
– Eggs and egg whites
– Grass-fed beef (use occasionally)
Healthy Fats (Focus on unsaturated sources):
– Avocados and avocado oil
– Olive oil
– Walnuts, almonds, macadamia nuts
– Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and pumpkin seeds
– Coconut products (consume in moderation)
Low-Impact Carbohydrates (High in fiber, low in sugar):
– Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and arugula
– Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts
– Low-sugar fruits such as blueberries and blackberries in small amounts
– Bell peppers, zucchini, and cucumbers
– Shirataki noodles or spiralized vegetables
How to Get Started With Keto 2.0
Making the shift to Keto 2.0 doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Follow these practical tips to ease into your new lifestyle:
1. Start Gradually: Reduce carb intake slowly to give your metabolism time to adapt.
2. Choose Whole Foods: Steer clear of packaged keto snacks. Opt for clean, nutrient-rich ingredients.
3. Track Your Macros: Use tools like MyFitnessPal or Cronometer to ensure you’re staying on course.
4. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water and monitor electrolytes. Supplement with magnesium, potassium, and sea salt if needed.
5. Focus on Holistic Benefits: Set goals that go beyond weight loss, such as improved digestion, stable energy, clearer skin, or better mood.
A Balanced Approach to Better Health
Keto 2.0 delivers a smarter, more sustainable alternative to traditional ketogenic dieting. By emphasizing whole foods, unsaturated fats, and plant-based nutrition, this approach supports not just fat loss but also overall well-being.
Whether you’re new to low-carb eating or seeking a reset from the strict confines of classic keto, Keto 2.0 offers a flexible and nourishing path to long-term health. With improved energy, heart health, and digestive wellness, this evolved keto lifestyle can easily fit into your daily routine.
Want more tools and support? Subscribe to our newsletter for weekly tips, recipes, and product spotlights that make Keto 2.0 even easier to follow.
References
1. Michalczyk, M. (2022). Interview featured in Women’s Health Magazine. Retrieved from https://www.womenshealthmag.com
2. Frontiers in Nutrition (2021). “Dietary Fat Intake and Cardiometabolic Disease Risk.” Retrieved from https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2021.689239/full
3. Menzel, J. et al. (2020). “Sustainability of the Ketogenic Diet — A Retrospective Study.” Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8887328
4. Cole, W. (2018). Ketotarian. Avery Publishing Group
5. edrugstore.com – Visit for lifestyle support, low-carb supplements, and expert-reviewed content. www.edrugstore.com